Healthcare Interoperability
What is the role of data for interoperability in healthcare?
Interoperability in healthcare is the ability for different information systems and applications to quickly communicate, integrate, and exchange secure data so it can be used to optimize better health outcomes for individuals and populations. The use of standards and data exchange models enables this information to be shared between healthcare providers, professionals, patients, hospitals, pharmacies, laboratories, etc., regardless of the application being used.
Why is interoperability important in healthcare?
For Providers
Interoperability gives providers easy access to more complete patient records, allowing for more informed care. Additionally, it helps providers more easily share relevant information with their peers/other providers including specialists, other clinics, hospitals, and more.
For Patients
Improving interoperability across the entire healthcare network, when paired with evolving legislation, will lead to better care. Patients will have ownership and insight into their entire medical history.
Ultimately, better healthcare data allows for interoperability and results in better care.
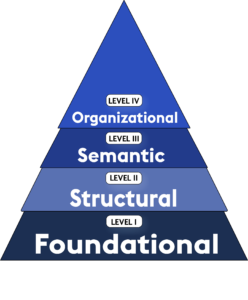
The HIMSS four levels of interoperability
 Interoperability in healthcare allows various healthcare information technology (HIT) to access, exchange, integrate, and communicate information. This is valuable for a number of reasons, including flexibility for organizations of varying maturities and creating holistic, portable patient and member records.
Interoperability in healthcare allows various healthcare information technology (HIT) to access, exchange, integrate, and communicate information. This is valuable for a number of reasons, including flexibility for organizations of varying maturities and creating holistic, portable patient and member records.
The Healthcare Information and Management System Society (HIMSS) created the following four levels of interoperability:
Level 1 – Foundational: Foundational interoperability establishes interconnectivity between HIT systems, allowing for secure data exchange.
Level 2 – Structural: Structural interoperability defines the format, structure, and syntax of data exchange. Structuring data in this way allows healthcare information to move between systems without losing the clinical or operational meaning of the data.
Level 3 – Semantic: Semantic interoperability combines standardized data structures, value sets, and vocabulary to simplify data interpretation. This standardization improves the quality, safety, and efficiency of healthcare delivery.
Level 4 – Organizational: Organizational interoperability facilitates secure and timely data sharing through governance, policy, and organizational regulations.
Benefits of interoperability in healthcare
The primary focus and end goal of interoperability in healthcare is to improve patient care and safety. It allows healthcare organizations to achieve their strategic goals and objectives. Here are five key benefits to interoperability in healthcare: