Healthcare Data Governance
What is data governance in healthcare?
Data governance in healthcare protects, secures, and accurately gathers your data to ensure it can be used correctly. The overall goal of data governance is to encourage organizations to transform data into insight.
Why is it important?
Without governance, your chances for sustaining your business improvements based on analytics diminishes rapidly.
Effective data governance focuses on all phases of data: creation, extraction, cleansing, storage (including backup, recovery, and replication), refining, analysis, transformation, and appropriate use. Hesitance to embrace data governance is common, and a value proposition for data governance must be developed prior to implementing governance policies, procedures, and processes.
Benefits of data governance in healthcare
High-quality data and effective data governance go hand-in-hand. Together, they have a substantial impact on your business, the communities you serve, and the future of healthcare innovation. Healthcare organizations and their patients can expect to see several benefits, including:
Successful data governance strategy
Some tried-and-true elements of a successful data governance strategy for healthcare organizations include:
Assign Accountability
Establishing accountability at your organization is the first step. A data governance committee consists of stakeholders from clinical, administrative, and financial or business departments. The committee is responsible for developing, implementing, and monitoring policies to ensure that all data is inventoried and subjected to the principles and processes that are part of governance.
Ongoing Data Management
As a primary responsibility of the data governance committee, this encompasses data storage, security, documentation, transfer, and all other uses for the data within your organization.
Revisit and Review
Keeping data clean and secure, and ensuring that your organization can make the most of its data requires continual review and maintenance. This includes periodic audits and specific reviews of data needs and policies. This is particularly important following business events like mergers and acquisitions, implementation of new systems or processes, or changes in workflows.
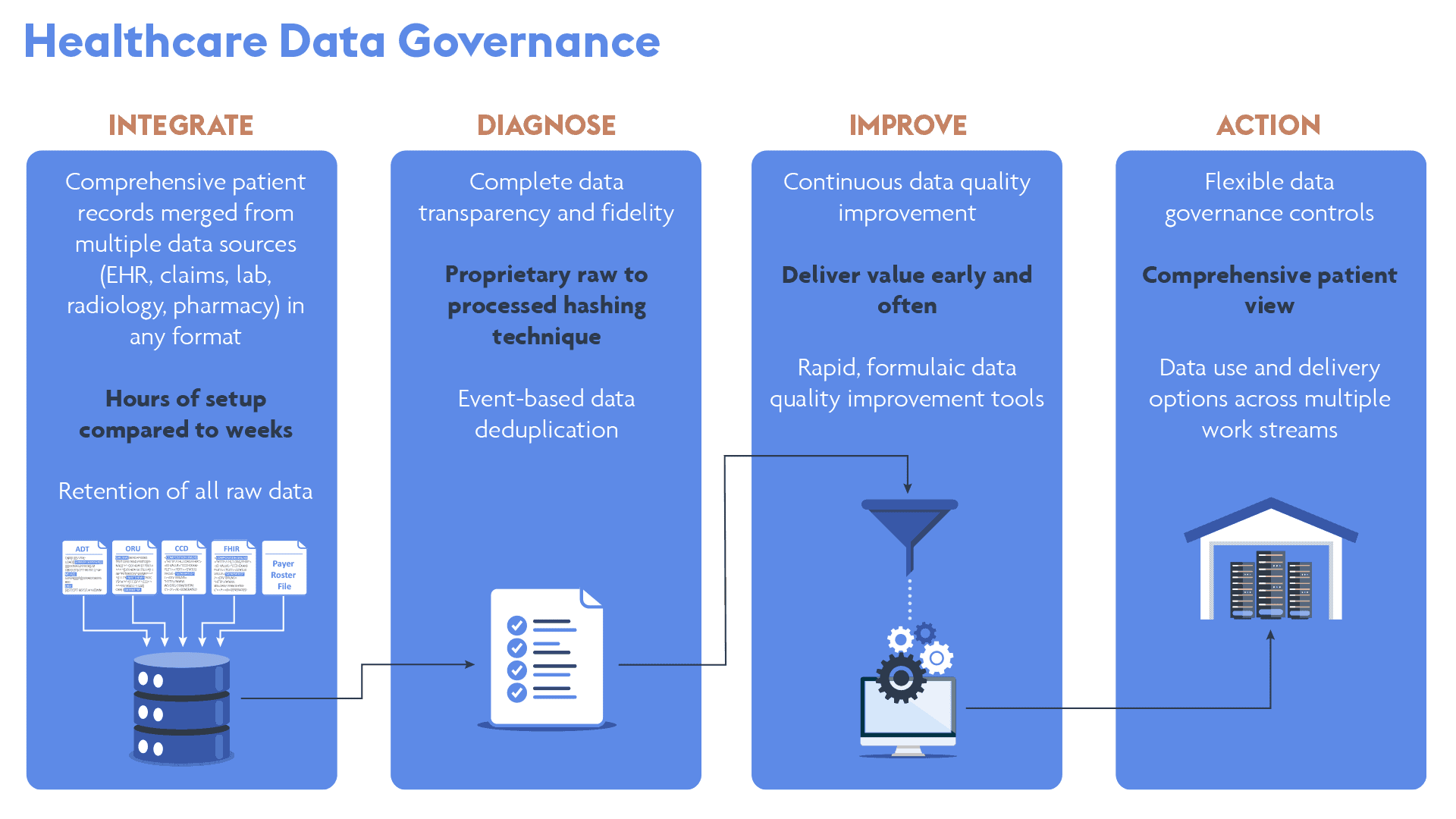
The Verinovum approach to data governance